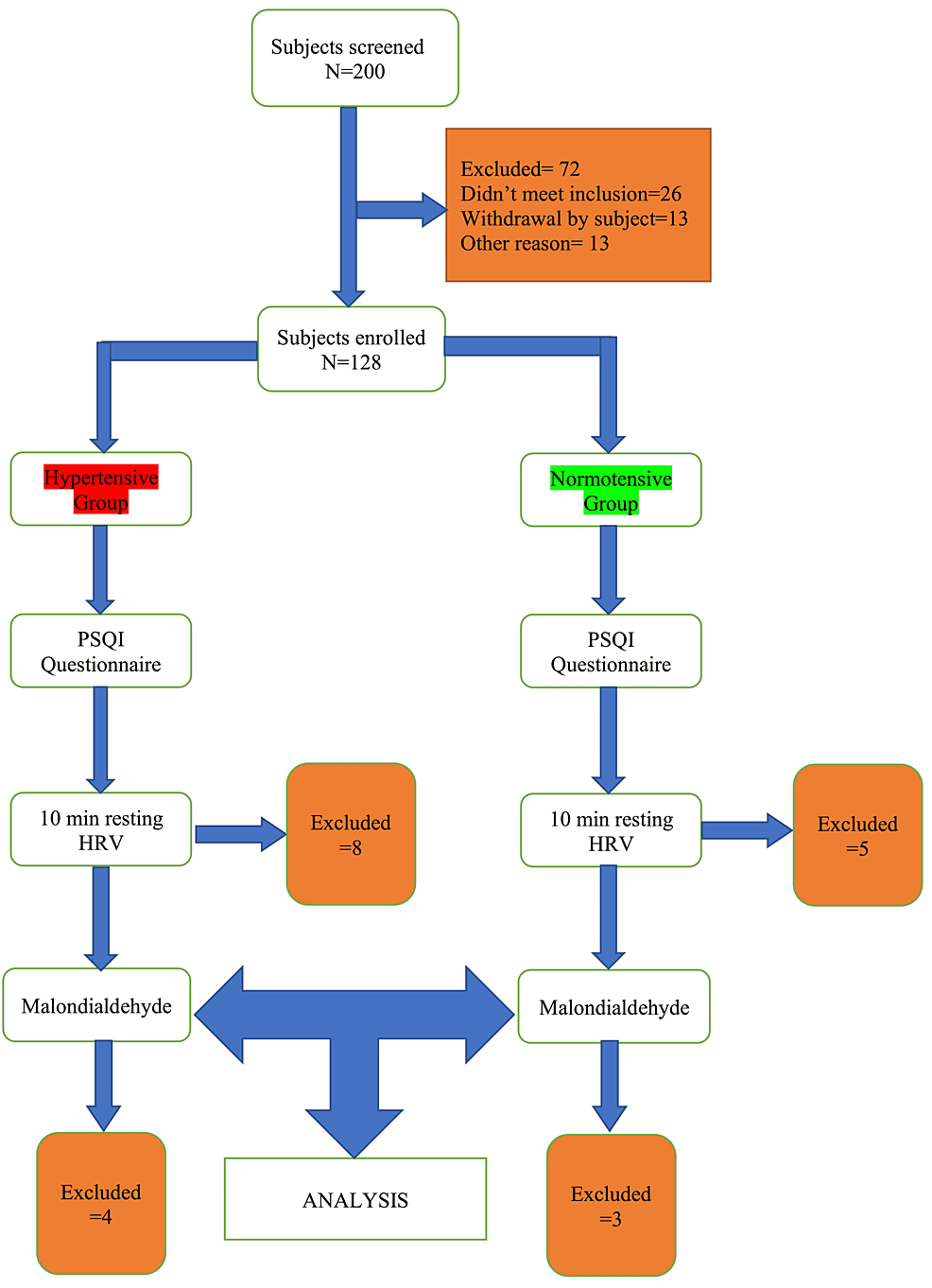
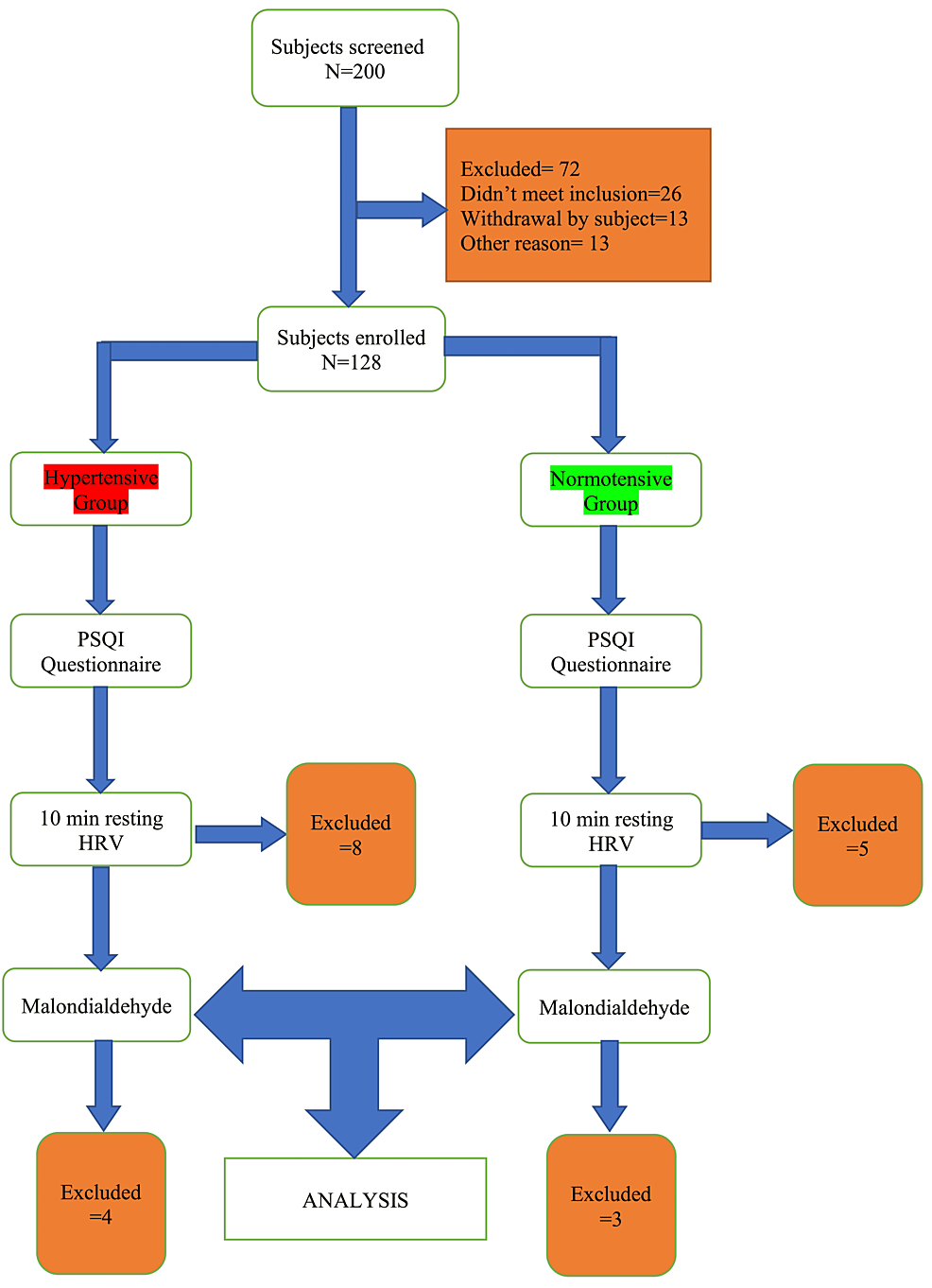
A Comparative Study of Baseline Heart Rate… Leave a comment
Malondialdehyde estimation
Sample Collection
Three millilitres of venous blood was drawn from each subject in a sterilised manner from the median cubital vein in a plain red vial (BD, USA). The whole blood was allowed to clot for 10 minutes before being centrifuged at 3000 rpm for five minutes to separate the serum, which was then collected in a sterile Eppendorf microcentrifuge tube (Eppendorf, Germany) and stored at −800 °C until the next procedure.
MDA Analysis
Instruments Used:
20 ml Graduated tubes
Ice filled Container
Centrifuge
Boiling Water Bath
Vortex
ELISA Plate
ELISA Reader
Reagents Used and Their Preparation
MDA: MDA is required to prepare different Standard concentrations based on which samples are quantified.
TCA: 20% TCA was prepared by weighing 20 g of pure solute Trichloroacetic acid in 100ml of DDW.
H2SO4: 0.05 M sulphuric acid was prepared by adding 2.8 mL of Concentrated Sulphuric acid in 1 litre of DDW.
Sodium sulphate solution: 2 M of sodium sulphate solution was prepared by dissolving 28.4 g of anhydrous sodium sulphate in 90 mL of DDW with constant heating and stirring. Further final volume is made to 100 mL with DDW.
TBA: 0.67% of thiobarbituric acid was prepared by dissolving 670 mg of TBA in 100 mL of 2 M sodium sulphate solution.
n-Butanol/n-butyl alcohol: Readily and commercially available n-Butyl alcohol was used.
Sterile/double distilled water
Standard Preparation
MDA Standard solution was prepared from 500 µM stock solution purchased (EZAssay TBARS Estimation kit, Himedia, India).
Working stock standard for MDA: Prepared by diluting 0.2 mL of stock solution in 10 mL of 0.05 M H2SO4 to obtain 10 µM working stock solution.
Different concentrations of standards were prepared by diluting working stock according to the following table:
Principle of MDA
Lipoproteins were precipitated from the serum sample by adding 20% TCA. The malondialdehyde present in the specimen reacts with thiobarbituric acid in sodium sulphate to form a pink-coloured complex. The intensity of the coloured complex directly depends on the concentration of MDA levels present in the serum sample.
The coloured complex developed was later extracted in n-butanol, which was finally read for the absorbance readings at 530 nm (green filter) using a colorimeter filter or ELISA reader. The method was standardised using various concentrations of standard solution, and a standard curve was plotted on graph paper for measuring the reading of test results.
Procedure of MDA Estimation
Three clean, dry, and labelled test tubes were arranged in the test tube rack, and the following were pipetted out carefully in respective tubes as in Table 7
| REAGENTS | TEST (µl) | STANDARD (µl) | BLANK (µl) |
| Serum | 250 | – | – |
| Standard (10μM/L) | – | 250 | – |
| Double Distilled Water | – | – | 250 |
| 20 % TCA | 1250 | 1250 | 1250 |
| Tubes were left to stand for 10 minutes at Room Temp | |||
| Tubes were then centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 mins | |||
| Supernatant was decanted, and the precipitate was processed with the following reagents. | |||
| 0.05M H2SO4 | 1250 | 1250 | 1250 |
| 0.67 % TBA | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 |
| All tubes were heated in a boiling water bath at 90oC for 30 minutes. | |||
| Tubes were then cooled on ice. | |||
| n-Butanol | 2 ml | 2 ml | 2 ml |
| With vigorous shaking, resulted chromogen were obtained. | |||
| Separation of organic phase by centrifugation at 3000rpm for 10 mins was done | |||
| The organic phase was filtered and 200 µl pipetted respectively in different wells of ELISA plate. |
Table 7: Detailed procedure for malondialdehyde estimation.
The ELISA plate wells were mixed well and read at 530 nm on the ELISA reader.
Patient case proforma
Participant no: Name:
Age/Sex: Religion
History reported by: Address:
Phone No: Occupation
Presenting complains: (with duration in chronological order)
HOPI:
Past history: (with details of treatment and outcome status)
Treatment history: (including details of outside hospital treatments)
Family and close contacts history:
Personal history:
1. Education-
2. Married/unmarried –
3. Occupation (monthly income, if any) –
4. Habits (details of smoking/alcohol) –
5. Details of hygiene habits (e.g., hand washing, disposal of sewage, etc.) –
6. Menstrual history (if female) –
7. Sexual history –
Any STDs – (details including cure)
8. Sleep pattern and mental status –
9. A dietary pattern including recent detailed food history up to 2 days before symptom onset-
10. Vaccinations status –
11. Travel history –
Social history: (including socioeconomic status, surrounding lifestyles, home and habitus, occupation)
Physical examination: (with consent and hand hygiene)
1. Mental status –
2. General appearance –
3. Vitals: PR – , RR – , BP – , Temp – SpO2 –
4. Skin – Height: Weight: BMI:
Inspections
Palpations
Percussions
Auscultation
5. Chest (respiratory system)
6. Chest (cardiovascular)
7. Abdomen
8. Genito-urinary-Rectal exam –
9. Musculoskeletal exam –
10. Neurological exam –
11. Investigation planned (to be sent for all participants)-
· Complete blood count
· Blood urea
· Serum creatinine
· Serum electrolytes (Na, K, Cl, Ca)
· Chest X-ray
· 12 lead ECG
· Urine analysis
· Plasma glucose