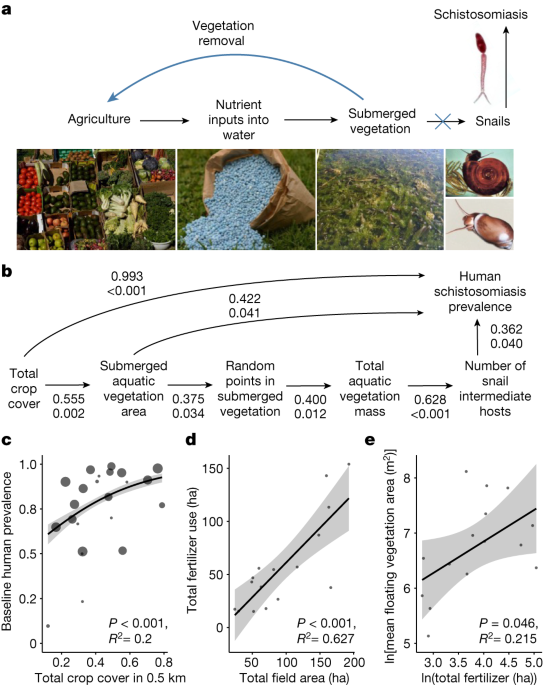
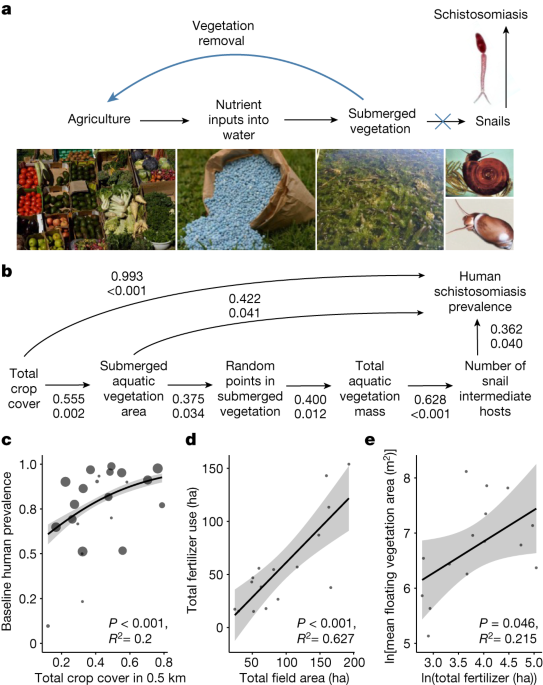
A planetary health innovation for disease, food and water challenges Leave a comment
Hotez, P. J. et al. Control of neglected tropical diseases. New Engl. J. Med. 357, 1018–1027 (2007).
Hotez, P. J. Neglected infections of poverty in the United States of America. PLoS Negl.Trop. Dis. 2, e256 (2008).
Ngonghala, C. N. et al. Poverty, disease, and the ecology of complex systems. PLoS Biol. 12, e1001827 (2014).
Barrett, C. B., Carter, M. R. & Chavas, J. The Economics of Poverty Traps (Univ. Chicago Press, 2019).
Lozano, R. et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380, 2095–2128 (2013).
Rohr, J. R. et al. Emerging human infectious diseases and the links to global food production. Nat. Sustain. 2, 445 (2019).
Halstead, N. T. et al. Agrochemicals increase risk of human schistosomiasis by supporting higher densities of intermediate hosts. Nat. Commun. 9, 837 (2018).
Steinmann, P., Keiser, J., Bos, R., Tanner, M. & Utzinger, J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 6, 411–425 (2006).
Gryseels, B., Polman, K., Clerinx, J. & Kestens, L. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 368, 1106–1118 (2006).
King, C. H. Parasites and poverty: the case of schistosomiasis. Acta Trop. 113, 95–104 (2010).
Whitmee, S. et al. Safeguarding human health in the Anthropocene epoch: report of The Rockefeller Foundation–Lancet Commission on Planetary Health. Lancet 386, 1973–2028 (2015).
FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP & WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World: Transforming Food Systems for Food Security, Improved Nutrition and Affordable Healthy Diets for All https://doi.org/10.4060/cb4474en (FAO, 2021).
Collecting and Carrying Water, Burdensome Reality for Women https://www.unwomen.org/en/news/stories/2014/3/collecting-and-carrying-water-burdensome-reality-for-women (UN Women, 2014).
Hoover, C. M. et al. Modelled effects of prawn aquaculture on poverty alleviation and schistosomiasis control. Nat. Sustain. 2, 611–620 (2019).
Haggerty, C. J. et al. Aquatic macrophytes and macroinvertebrate predators affect densities of snail hosts and local production of schistosome cercariae that cause human schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl.Trop. Dis. 14, e0008417 (2020).
Wood, C. L. et al. Precision mapping of snail habitat provides a powerful indicator of human schistosomiasis transmission. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 23182–23191 (2019).
Underwood, G. J. C., Thomas, J. D. & Baker, J. H. An experimental investigation of interactions in snail–macrophyte–epiphyte systems. Oecologia 91, 587–595 (1992).
Global Invasive Species Database, http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=281 (accessed November 2022).
Best, E. P. Effects of nitrogen on the growth and nitrogenous compounds of Ceratophyllum demersum. Aquat. Bot. 8, 197–206 (1980).
Pietro, K. C., Chimney, M. J. & Steinman, A. D. Phosphorus removal by the Ceratophyllum/periphyton complex in a south Florida (USA) freshwater marsh. Ecol. Eng. 27, 290–300 (2006).
Quilliam, R. S. et al. Can macrophyte harvesting from eutrophic water close the loop on nutrient loss from agricultural land? J. Environ. Manage. 152, 210–217 (2015).
Lo, N. C. et al. Impact and cost-effectiveness of snail control to achieve disease control targets for schistosomiasis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, E584 (2018).
WHO. Prevention and control of schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 912, 57 (2002).
Chu, K. Trials of ecological and chemical measures for the control of Schistosoma haematobium transmission in a Volta Lake village. Bull. World Health Organ. 56, 313 (1978).
Deol, A. K. et al. Schistosomiasis—assessing progress toward the 2020 and 2025 global goals. New Engl. J. Med. 381, 2519–2528 (2019).
Klumpp, R. & Chu, K. Importance of the aquatic weed Ceratophyllum to transmission of Schistosoma haematobium in the Volta Lake, Ghana. Bull. World Health Organ. 58, 791 (1980).
Boelee, E. & Laamrani, H. Environmental control of schistosomiasis through community participation in a Moroccan oasis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 9, 997–1004 (2004).
Garchitorena, A. et al. Disease ecology, health and the environment: a framework to account for ecological and socio-economic drivers in the control of neglected tropical diseases. Phil. Trans. R Soc. B 372, 20160128 (2017).
Liu, Z. Y.-C. et al. Deep learning segmentation of satellite imagery identifies aquatic vegetation associated with snail intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis in Senegal, Africa. Remote Sens. 14, 1345 (2022).
Jones, I. J. et al. Schistosome infection in Senegal is associated with different spatial extents of risk and ecological drivers for Schistosoma haematobium and S. mansoni. PLOS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 15, e0009712 (2021).
Sustainable Development Goals https://sdgs.un.org/goals (United Nations, 2021).
Hopkins, S. R. et al. Evidence gaps and diversity among potential win–win solutions for conservation and human infectious disease control. Lancet Planet. Health 6, e694–e705 (2022).
Leonardi, U. Senegal Land Cover Mapping, Technical Report. http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/geospatial/docs/Land_Cover/Senegal_LC/Senegal_LC_Report_1208.pdf (FAO, 2008).
Moher, D. et al. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int. J. Surg, 10, 28–55 (2012).
Plouvier, S., Leroy, J. C. & Colette, J. A propos d’une technique simple de filtration des urines dans le diagnostic de la bilharziose urinaire en enquête de masse. Med. Trop. 35, 229–230 (1975).
Katz, N., Chaves, A. & Pellegrino, J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in Schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 14, 397–400 (1972).
Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences. International ethical guidelines for biomedical research involving human subjects. Bull. Med. Ethics 182, 17–23 (2002).
Venables, W. N. & Ripley, B. D. Modern Applied Statistics with S 4th edn (Springer, 2002).
Lefcheck, J. S. piecewiseSEM: piecewise structural equation modeling in R for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 7, 6 (2016).
Wickham, H. The split-apply-combine strategy for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 40, 1–29 (2011).
Brooks, M. E. et al. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 9, 378–400 (2017).
Fox, J. & Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression (Sage Publications, 2018).
Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (Springer, 2016).
Lenth, R. V. Least-squares means: the R package lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. 69, 1–33 (2016).
Huang, F. L. Alternatives to logistic regression models in experimental studies. J. Exp. Educ. 90, 213–228 (2022).
Anderson, M. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods (Primer-E, 2008).
Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-modal inference. Model selection and model averaging based on information criteria (AICc and alike). (2019).
Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated marginal means, aka least-squares means. R package version 1.4.7. (2020).
Christensen, R. H. B. ordinal: Regression models for ordinal data. R package version 2019.12-10 (2019).
Best, P. Nutrient content of the aquatic macrophytes Elodea canadensis and Ceratophyllum in the course of the year. Hydrobiol. Bull. 10, 15–16 (1976).